Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
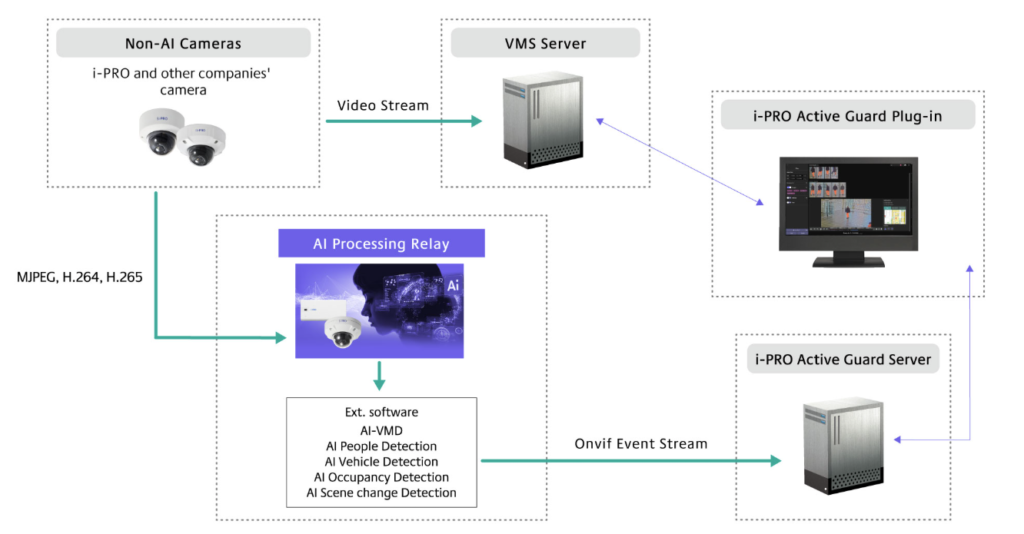
Computer Vision at the Edge enables machines to interpret visual data instantly, right where it is captured.
By combining computer vision with edge computing, organizations can analyze images and video streams directly on local devices such as cameras, sensors, or embedded systems. This approach removes the need to send large volumes of visual data to centralized servers, allowing faster responses and more efficient operations.
Edge-based visual intelligence is becoming essential as the volume of video data grows and real-time decision-making becomes critical across industries.
Understanding Computer Vision at the Edge
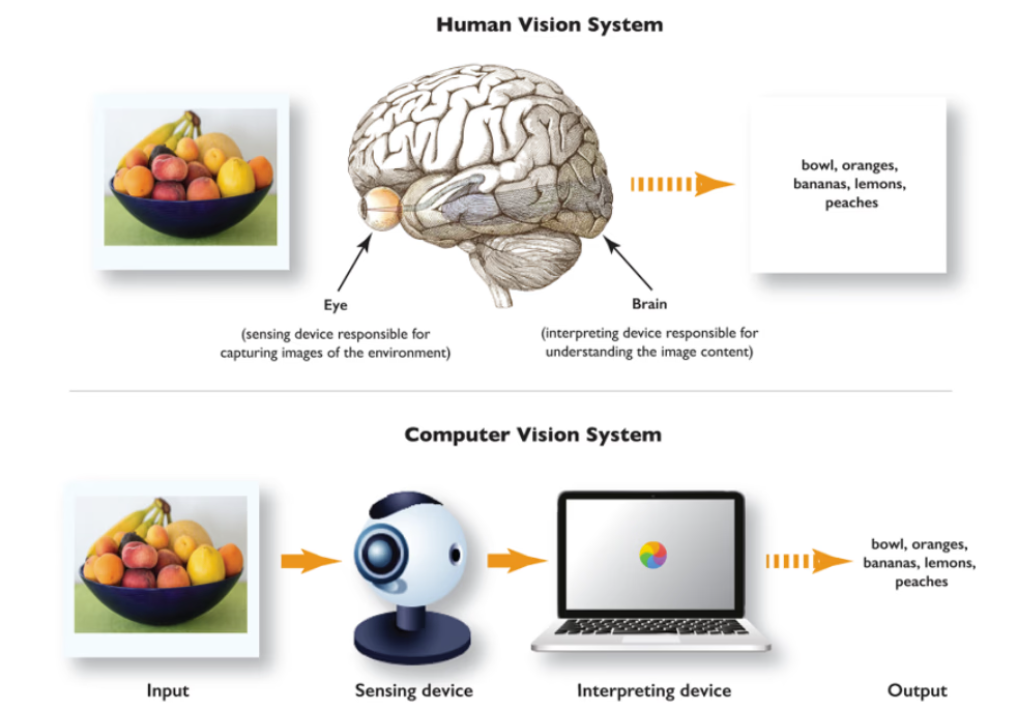
Computer vision at the edge refers to deploying vision algorithms directly on or near data-generating devices rather than relying solely on cloud infrastructure. In traditional models, visual data is transmitted to the cloud for processing, which can introduce latency, increase network costs, and create privacy concerns. Edge-based systems shift this processing closer to the source, enabling immediate interpretation and action.
This localized processing allows systems to detect patterns, recognize objects, track movement, and identify anomalies without depending on constant connectivity. The result is faster, more resilient, and more autonomous visual intelligence.
Real-Time Intelligence and Responsiveness
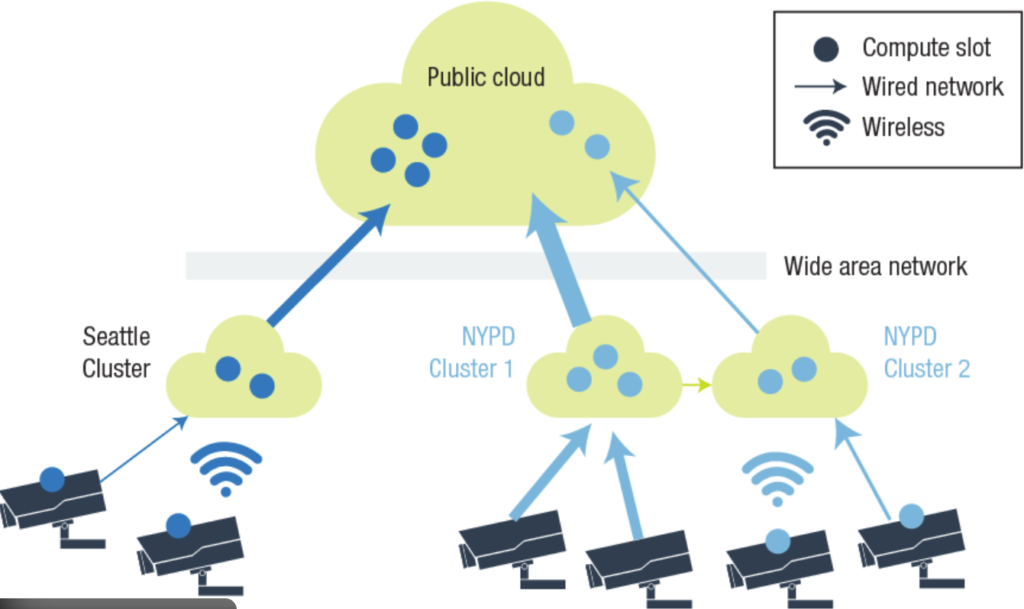
A major advantage of edge computer vision is its ability to deliver insights in real time. Since visual data does not need to travel back and forth between devices and remote servers, decisions can be made within milliseconds. This is especially important in environments where delays could lead to safety risks, quality issues, or operational inefficiencies.
Real-time processing enables immediate responses such as stopping machinery when a defect is detected, triggering alerts during unsafe conditions, or adjusting systems dynamically based on what the camera sees. These capabilities are difficult to achieve with cloud-only vision systems.
Privacy, Security, and Bandwidth Efficiency
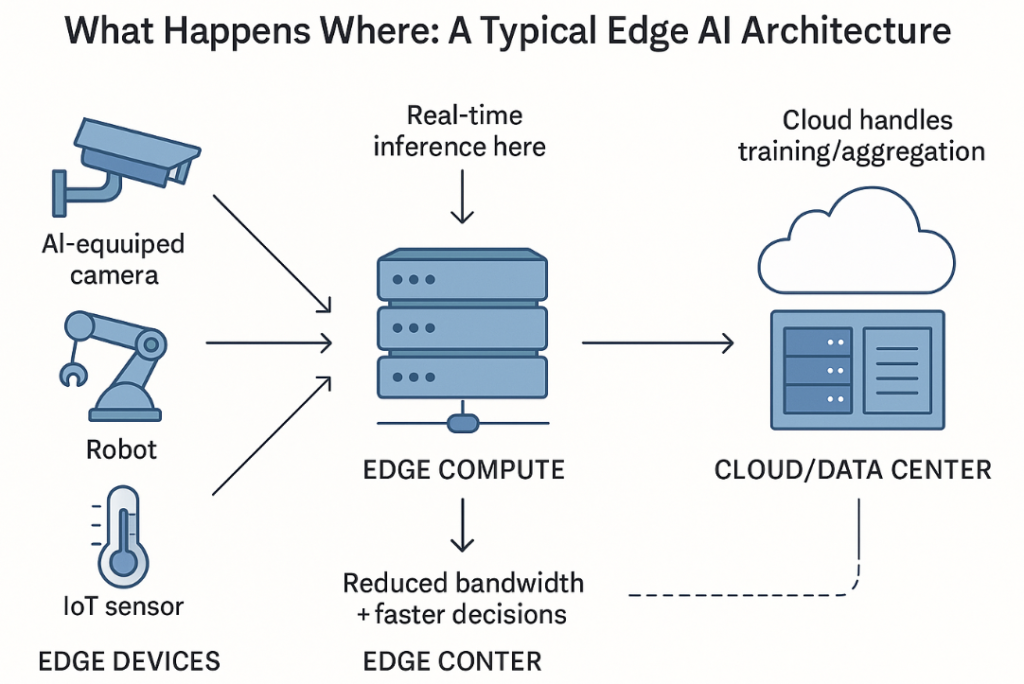
Processing visual data at the edge also improves privacy and security. Since raw images and videos can remain on the device, the exposure of sensitive data is significantly reduced. This is particularly valuable in regulated environments where data movement and storage are tightly controlled.
In addition, edge computer vision reduces bandwidth consumption by transmitting only relevant insights instead of continuous video streams. This lowers network costs and allows systems to operate effectively even in locations with limited or unreliable connectivity.
Industry Applications of Edge Computer Vision
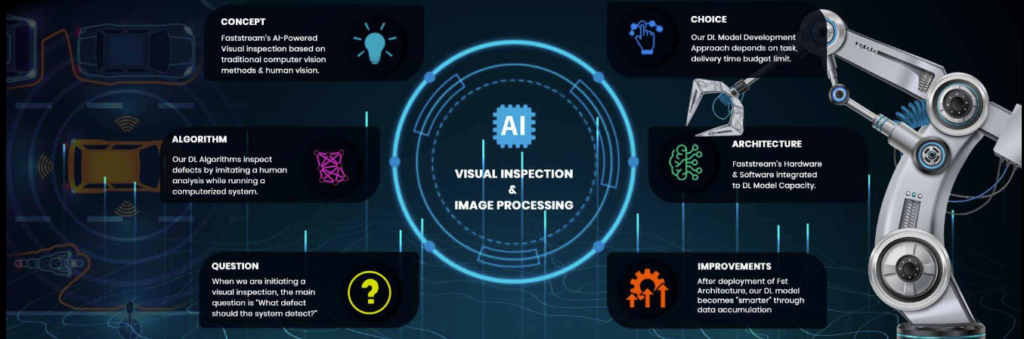
Across industries, edge computer vision is enabling smarter and more autonomous systems. In manufacturing, it supports automated inspection and quality control by detecting defects as products move through production lines. In smart cities, cameras analyze traffic patterns and safety conditions in real time to improve mobility and reduce incidents.
Retail environments use edge vision to monitor shelves, understand customer movement, and enhance in-store operations. Transportation systems rely on edge-based vision for vehicle perception and safety monitoring. In many cases, these systems operate independently while selectively sharing insights with cloud platforms for long-term analysis and model improvement.
As hardware becomes more powerful and AI models more efficient, computer vision at the edge will continue to expand. Future systems will be able to process increasingly complex visual tasks while consuming less power and operating in smaller form factors.
By bringing intelligence closer to where visual data is created, edge computer vision lays the foundation for faster decisions, safer environments, and more efficient digital systems. It represents a practical and scalable approach to visual AI in a world where real-time insight is no longer optional.